What is Ransomware?
Ransomware has easily become one of the most popular cyber security threats over the last few years. It has affected countless individuals and every industry you can think of: education, finance, municipal, etc. and it doesn’t look like attacks are slowing down anytime soon. In this article we will dive into what exactly ransomware is and how you can protect yourself from it.
Ransom Note
Probably somewhat of an obvious motivation for hackers is financial gain. We’ve seen countless times in the news (or you may have experienced it yourself) when hackers have stolen credit card information, or other financial documents in order to get some sort of monetary value out of their hack. In fact, it is estimated that by 2025 cybercrime is going to cost the world up to 10.5 trillion dollars annually. That’s not a small number. That’s about roughly 1/9th of the world’s GDP, and about half of the United State’s GDP.
When it comes to hacking, we need to think more broadly about what represents value. In the real world we have tangible things that are worth value depending on who the thing belongs to; jewelry, artifacts, shoes, etc. If we’re thieves, this is what we may target. In cyber space things change a bit. A document that contains personal information may be considered valuable. In the case of many companies all over the globe, intellectual property stored on a server is a great example of something that is considered a high valued asset. To a hacker, these are all items that stand out as good targets.
Let’s say you woke up one day and were presented with this screen at your desktop:
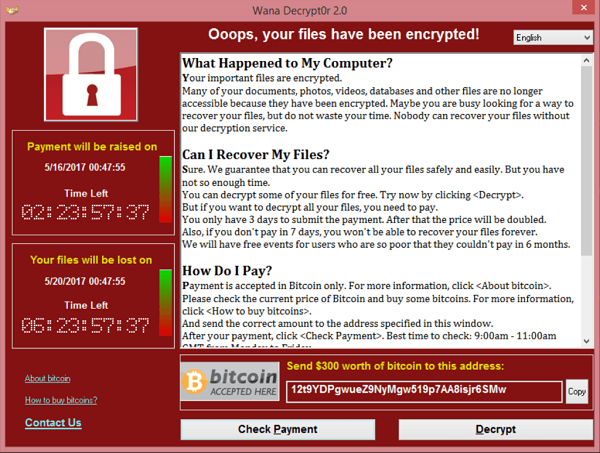
Your first reaction would probably be one of shock, but maybe disbelief. You then try to access files on your computer and they are all “locked.” You now realize that you’ve been hit with ransomware. This is the exact prompt many companies and individuals were hit with back in 2017 when the WannaCry Ransomware attack made its way into the cyber world. This attack was highly distributed and just one of many ransomwares out there that have caused havoc. We’ll break down the components of ransomware in the next section.
Get Your Files Back!
Let’s look at the above screenshot. It claims you can get your files back if you pay a certain amount in bitcoin. It also claims the pay amount will raise after a certain amount of days, and after 7 days your files will be gone/unaccessible permanently. This sounds eerily like a normal kidnapping scenario. Much like a kidnapper would demand ransom for the person they just kidnapped, we can see the similiarties in how a hacker may do the exact same thing but with someone’s computer files. So how does ransomware work?
We can break down ransomware by first addressing its main component, encryption. If you want to learn more about encryption, check out my “What is Encryption” article. Essentially, this is the hacker’s way to control the entire situation. If they are able to encrypt your files, only they (presumably) would have the key to unlock them. Towards the end of my encryption article, I hinted that this is the main crux of encryption. When implemented correctly it works very well, which may have negative implications for people that need to access that information.
Ransomware falls under the category of malware. It is designed to search through your computer and encrypt as many files as possible. In addition, it also can include any necessary component to have the hack be succesful in the long run; for example this could include some kind of command and control infrasturcture and a way to propagate throughout the network to infect other computers. The more sophisticated the ransomware is, the more parts it will have to it.
The WannaCry ransomware attack was very unique in the fact that it used vulnerabilites and exploits that were stolen from the NSA to make itself very effective at spreading. If you want to read the details of the attack, check out this article.
The final component of all ransomware is the ransom part. Depending on the type of ransomware, you may see different amounts of money being asked for by the hackers. These ransoms can go from a couple hundred dollars to the hundreds of thousands (even millions in some cases). If a company has been breached, you have to think of the ransom in addition to the downtime the company experienced. For businesses, time is literally money. It may cost a company more money to recover what they lost as opposed to the ransom payment itself. Here’s a great article detailing ransomware specific attacks and the various entities it has affected.
Most ransomware attacks will demand payment in the form of cryptocurrency. TL;DL, cryptocurrency is a form of online currency that can be used to purchase things. Bitcoin is a prime example of a well known cryptocurrency. Part of the lure of cryptocurrency is in its ability to keep a buyer/seller anonymnous in the transaction. While bitcoin itself is not anonymous, hackers will use methods to route their bitcoin through various places to throw investigators off. Remember, they’re not trying to get caught, and precautions against that are necessary.
We caught you…
While businesses have been prime targets for ransomware attacks for years, every day people are not immune either. When targeting individuals, a certain branch of ransomware called “fearware” may be used to socially engineer them to go through with the ransom. Take a look at this fearware example:

This is certainly a different message being shown to us than the WannaCry example. Now instead of holding your files hostage and demanding a ransom, they’ve added the possibility of being arrested for alleged serious crimes. To the unsuspecting person, the threat of an arrest may be just enough to get them to pay the ransom. This is similiar to a spoofing email where the user may be pretending to be an authorative figure to illicit a response. In this case however, they have locked you out of your computer completely, which is something you might think the FBI can actually do.
Nonetheless they ask you for payment in the form of either cryptocurrency or gift cards. This is where the suspicious side of you needs to kick in. The FBI would never announce an arrest of you if the charges they claimed in the details were true. They would also never ask for your money, especially in the form of a gift card for example. The ridiculousness of the prompt SHOULD be proof you shouldn’t pay the ransom. Even if you do pay it, there’s no guarantee the hacker will unlock your files/computer. So how do you protect yourself from ransomware?
Back that A:\SS up
Unlike in the real world, having two of something very unique is trivial in cyber space. I can easily copy sensitive documents or entire hard drives of information and put it somewhere else. I cannot do this with a historical artifact for example. Having a backup of your files can make the difference between complete ruin and a simple system reimaging. Of course, backing up your files has more applications than just a reaction against ransomware. Part of having good cyber hygeine is keeping the availibility of your systems high. This way way if you run an organization and are hit with ransomware or another disaster, you can easily reimage and transfer the backup(s) to the machine(s) involved.
Whether you choose to use a physical backup or cloud, you should make sure those are kept properly secure:
Physical Backup(i.e external hard drive):
Pros
- You own the device, which means nobody else can manipulate it unless they have physical access to it
- It is usually speedier to read/write from disk than download and upload over the internet with the cloud
Cons
- If your only physical backup is compromised(breaks, stolen, etc.), you’re screwed
- You many have to add more hardware to keep up with storage needs, which may be costly
Cloud Backup(Google, Dropbox, etc.):
Pros
- Data can be accessed from anywhere that has internet access
- You don’t have to manage your own hardware infrastructure, and simply pay a monthly fee for however much cloud storage you need
Cons
- If the internet is not accessible, you cannot access your data
- Subject to potential cloud storage vulnerabilites on the internet
For individuals, backuping your important files such as photos or messages might just be as simple as using iCloud or another program. You can also buy an extended hard drive for your personal computer and backup all important files to it if you prefer having physical storage. For companies, a lot more needs to be put into the backup and recovery process. Ideally, using a hybrid method of physical and cloud storage is the preffered way to go. Data loss, in most cases, is a company’s highest priority. This is why it is pivital that there is a plan of action in case of emergencies such as ransomware or a natural disaster.
Wear a mask!
Ok maybe you can’t prevent a computer from getting a virus by putting a mask on it, but you can with an antivirus/malware program. Over the years it has been increasingly difficult for antivirus software to keep up with the number of threats out there. However, having an antivirus program of some sort will still protect you from known threats, which is always a good thing. I’ll have a more in depth article about what a virus is in general, but for now you can trust that you need antivirus sofware as endpoint proctection in some capacity.
Don’t touch that
This has been talked about in many of my other articles, but is still relevant for this topic:
Clicking on suspicious links in email or a sketchy website probably isn’t the most ideal thing for your computer’s overall hygiene. It is imperative that you are aware of what you are clicking on and verifying the source of the download/link redirect. Remember, hackers are trying to work less. If it means socially engineering you to click on a link to download a malicious program, then they will do it. Unless the particular piece of ransomware is spreading through exploits of a program/service (i.e. WannaCry), you more than likely will encounter ransomware by not adhering to common sense internet behavior.
Hopefully after reading this article you have a good understanding of what ransomware is and how it affects the cyber security landscape. As more high profile companies are being targeted, the need for adequate cyber security defenses is going to increase. If you’re ever curious, you should ask your company what security measures they have in place to stop threats like ransomware. Thank you for reading!

